Stories in Science Special Series
Warm Waters and White Sand Beaches: My Journey Studying Human Impacts on the Ocean
I am a climate scientist, with one foot in the modern ocean trying to understand impacts on California species and ecosystems, and one foot in the past, probing the paleoclimate world for lessons we can learn.

Tessa Hill, Ph.D.
[su_boxbox title=”About Dr. Tessa Hill ” box_color=”#2668D5″]Dr. Tessa Hill is a Professor and Chancellor’s Fellow at the University of California, Davis, in the Department of Earth & Planetary Sciences. The story below was originally published in Medium on Dec 22 2017. You can follow her on Twitter @Tessa_M_Hill and explore her work the Hill Biogeochemistry Lab [/su_boxbox]
[dropcap]I[/dropcap]n September 2017, Category 5 Hurricane Irma bore down on the Leeward Islands of the Caribbean, raking across Barbuda before moving on to Anguilla, St. Maarten, the US Virgin Islands, the British Virgin Islands, and then setting a course for Cuba. After departing Cuba as a Category 4 hurricane, Irma then continued a wide swath of damage across the Florida Keys, the Gulf Coast, eventually making a mark on essentially the entire state of Florida. Storm surge flooding was experienced in the Keys, Miami, Naples, and all the way north to Jacksonville. This hurricane followed quickly on the heels of another historic event in the U.S., Hurricane Harvey, which brought unprecedented rain and flooding to Houston and eastern Texas, and preceded Hurricane Maria, one of the most destructive hurricanes in Caribbean history.
In the weeks between these events, we experienced a heatwave in Northern California, where temperatures topped 100 degrees multiple days in a row, and skies were so smoky from distant wildfires as to be dangerous. I sat slightly transfixed in the California heat, watching images of Harvey, Irma, then Maria take over my TV screen and social media streams. Much has been written about how these events are connected to climate change: quite simply, our chances of experiencing extreme conditions (heat, rainfall, intense hurricanes, drought) have gone up, because these hazards intensify in a warmer world. When I was beginning my scientific career nearly two decades ago, it was popular amongst senior scientists to refer to climate change as “the great human experiment.” An experiment that may have seemed largely theoretical at the time, but one we would all bear witness to in the future. Left unspoken was the burden that we scientists would carry in the knowing and bearing witness: how does one document the process without absorbing the impact?
Part I: The year that made climate change personal
I am a climate scientist, with one foot in the modern ocean trying to understand impacts on California species and ecosystems, and one foot in the past, probing the paleoclimate world for lessons we can learn. Much has changed over the 15+ years I have called myself a climate scientist, and yet more has stood still: While we continue to amass evidence for the role of human impact on the climate, and for the grave consequences of climate change, policy action in the U.S. has not responded to that evidence. Scientists continue to struggle with our role as producers of objective knowledge or advocates for evidence-based solutions for climate change, while the systems that we have studied for decades have degraded before our eyes. We are simultaneously bombarded with information about how rapidly our Earth is changing and with political arguments for inaction that attack the evidence, the scientists, and the scientific process. People often ask me if I spend time feeling sad about our trajectory or whether I manage to stay optimistic. Generally my answer is: I spend about ⅔ of my time trying to understand climate change and the impact on the ocean, and about ⅓ of my time trying to communicate those findings to students, policymakers, and the public. There isn’t much time for grief. But in the midst of the 2017 hurricane season, for the first time in a very long time, I felt really gutted by the destruction of places I had formerly lived, loved and visited. I couldn’t quite put my finger on why, until I started thinking about my path to becoming a scientist.
Although I often tell people I was “born a scientist” by being raised on the water in the Pacific Northwest, my scientific curiosity really blossomed on the Gulf Coast of Florida, at Eckerd College. I moved there, drawn by the sunny days, water that was a welcoming temperature, and the promise of spending my college years learning about marine science. I was so motivated towards this goal that the summer after my freshman year I volunteered to help a graduate student from another university with her research on dolphins in Jacksonville. That summer I packed everything I owned into a car – a sleeping bag, some boxes of household stuff, a few boxes of clothes, and drove to Jacksonville to spend a month sleeping on the floor of another student’s apartment. All of this effort was so that I could get up and work on a boat all day identifying and observing dolphins. The work, despite sounding glamorously Cousteau-esque, was filled with long hot days tossed around on a small boat with no shade, fortunately surrounded by dolphins and other dolphin loving students. Days that were not on the boat were spent peering over a light table to examine photographs of dolphins and trying to match them to a photo book that had hundreds of photos of dolphin fins. It was all dolphins, all the time, and it was my first real exposure to the level of dedication and love that scientists bring to their work.
I returned to college the next fall completely hooked on research, although surprisingly, not hooked on dolphins. I began to work on a research project with a professor trying to understand the environment of the Gulf Coast. This work often included days spent on a boat (again!), but also an equal amount of time in the lab washing glassware, sorting samples, labeling vials, and peering into a microscope at tiny fossils. My mentor was creative, funny, inspiring, and he pushed me hard to think about interesting questions in science. I began to develop my own small component of that project that he would encourage me to lead, looking at evidence that the islands that rimmed the Florida shoreline had moved as sea level rose over the past several thousand years. In sediment cores – long tubes of sand that we collected from the ocean floor – we would look for evidence of environmental change through time, using both the sand and tiny fossils to describe the ocean’s history. It was through this project that I discovered that mud deposited in the ocean could tell a story of the past. As sea level changed, the barrier islands moved too, staying parallel to and near the moving shoreline. These islands – the ones we build homes and roads on because we think of them as static features of the Gulf Coast shoreline – were actually moving objects, subject to the whims of changing seas. During my senior year in college, I began to ask my professors: could the record of past climate change tell us something about what will happen next?
* * *
That is what drew me to graduate school: wondering what the past would tell us about our future. At UC Santa Barbara for my Ph.D., I studied paleoclimate: essentially how we can reconstruct and investigate climate change in the Earth’s past. I was quite literally immersed in a community of scientists thinking, living, and breathing the past record of climate change. All the while, the picture of modern climate change was becoming clearer around us. The evidence was building, and while by day we were reading about climate change that had happened thousands or even millions of years ago, by night we would stay up reading the newest report of the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. The weight of what we were studying was beginning to become clear, and I began to get the first taste of the science communication challenge that lay ahead: publicly acknowledging that I studied past climate change was likely to inspire uncomfortable conversations with strangers and family members alike. Even worse was the worry that came with deep insights into the past: how the Earth’s climate system had shifted before due to changes in greenhouse gases, including rapid shifts in sea level, ocean temperature, and weather patterns. I remember one conversation in particular, in the main office of my department amongst a group of graduate students. One student insisted that the only way we could do something positive with our growing understanding of the Earth’s climate system was to leave science and work in environmental advocacy. I made an impassioned plea for why we desperately needed scientists to discover the mechanisms and impacts of climate change. He disagreed and insisted that we couldn’t cloister ourselves inside of universities only to gain more knowledge, and little action, on climate change. Our fellow students watched our debate like it was a ping pong match, but there was no easy resolution: do we discover new knowledge, or try to motivate societal change?
As I finished up graduate school in Santa Barbara, my husband and I were offered jobs in Northern California. As we prepared to buy a house, pack up our two bedroom apartment and move to a place that I had only visited once, we decided to take a last vacation before starting our jobs. We chose the islands of Anguilla and St. Maarten as our destination, looking forward to some needed relaxation before the next chapter of our lives began. We were there in the off season – who travels to the Leeward Islands in peak hurricane season? – which meant that day after day we had entire beaches to ourselves. Just us, the turquoise water, and the man frying johnny cakes in a stand on the side of the road. We practically lived in the Caribbean Sea that week – swimming and snorkeling day and night, only to hop in a car and drive to a new ocean-facing location. One day, a taxi driver in Anguilla recommended that we check out a spot called “Junk’s Hole Beach”. We laughed at the idea that a beach would be called a “Junk Hole”, and hopped in. The taxi dropped us off at the end of a gravel road, and when we arrived, the beach was empty, stunning, and the water beckoned. We began to walk the beach and came to a harsh realization about the name of the beach. Unlike the pristine beaches that we had been visiting over much of the island, due to prevailing winds and currents, this beach was completely covered with trash that had washed up from waste dumping offshore. Plastic pens, toothbrushes, water bottles, dead fish, fishing line, all tangled in a mess of seaweed and coral rubble. Here, alone on a beach on a windy day, on a beautiful, quiet island filled with warm and hospitable people, the fingerprint of human impacts on the ocean pressed upon us.
* * *
What I came to realize is that Hurricane Irma in particular stitched together a pattern of places that had influenced my view of the ocean, science, and human interaction with the environment. Leeward Islands. Florida’s Gulf Coast. Jacksonville. Warm waters, white sand beaches, and the birthplace of my oceanographic career. Simultaneously, I noticed that this year brought a new new kind of discussion among scientists: How, as a scientist, do you spend decades working to understand coral reefs, Arctic ice sheets, or kelp forests, only to end up being the person that records and reports the downfall of these systems? Scientists are trained through years of schooling to design methodologies that maintain their distance from their subjects and the outcomes of their experiments. For many years, that buffer of distance has kept us from absorbing the emotional toll of what we were observing, but the burden of being witness to this catastrophe was bound to catch up with us. I recently asked a colleague who is studying coral reef conservation how the past few years have felt. She described sitting back at a recent workshop and realizing that scientists were discussing a world that had moved beyond corals; a “post coral” ecosystem. Upon hearing this, I asked her: Does anyone ask you – what does it feel like to record the demise of your study system? She answered that most people don’t ask. Perhaps it is just too hard for scientists, journalists, policymakers and educators to go down this path.
While watching images from Houston, Florida and the Caribbean, what I saw was this: the great human experiment is the complete destruction of livelihoods and places we love. It is the death of people, businesses, and communities. It is not equally distributed, as it does its worst to the most impoverished communities. It is stranded pets and polluted waterways. It is multiple major disasters for our Federal Emergency Management Agency, our Coast Guard, our firefighters, our first responders. It is kids missing school days due to natural disasters and endless fundraisers to try to rebuild our communities. It is years of coral reef restoration blown away by the most powerful storm on record. It is the beginning of a mass migration, where those with resources will choose places to live based upon perception of risk due to flood, fire, storm surge and more. For me, 2017 was the year that I came to terms with how personal climate change might be, for all of us, and that we needed to start putting words to that experience.
Find Part II of this story here:[su_button url=”https://medium.com/@tmhill/when-climate-change-knocks-on-your-door-what-will-you-say-5bbdbb68f4ed ” target=”blank” icon=”icon: external-link”]Read Part II [/su_button]
More about Dr. Hill: Obama Honors Tessa Hill as Extraordinary Early-Career Scientist
Cover Image by Michelle Maria from Pixabay | CC0 Creative Commons
The CS Media Lab is a Boston-anchored civic science news collective with local, national and global coverage on TV, digital print, and radio through CivicSciTV, CivicSciTimes, and CivicSciRadio. Programs include Questions of the Day, Changemakers, QuickTake, Consider This Next, Stories in Science, Sai Resident Collective and more.

-
Audio Studio1 month ago
“Reading it opened up a whole new world.” Kim Steele on building her company ‘Documentaries Don’t Work’
-
 Civic Science Observer1 week ago
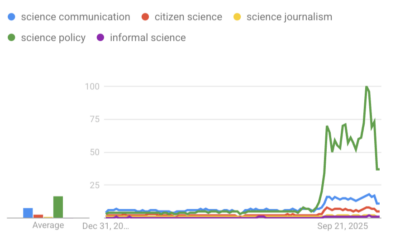
Civic Science Observer1 week ago‘Science policy’ Google searches spiked in 2025. What does that mean?
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Our developing civic science photojournalism experiment: Photos from 2025
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Together again: Day 1 of the 2025 ASTC conference in black and white
Contact
Menu
Designed with WordPress