Stories in Science Special Series
What Do You Want to be When You Grow Up?
The good thing about hitting rock bottom is that the only option left is to emerge. And that’s what I did.

– Luis Alberto Condori –
[su_boxbox title=”About” box_color=”#262733″]Luis is currently a college senior in Environmental Engineering in Bolivia, a member of the NGO ECOTEC, and works in Industry Solutions, a company that helps micro and small business develop by providing industrial machinery and engineering services. The story was translated from Spanish to English by Yara Rodriguez. [/su_boxbox]
[dropcap]M[/dropcap]ost of us have all been asked what do you want to be when you grow up when we were children. An Astronaut, a doctor, a police officer, and a football player were the most common answers in my environment. When I had to answer such an interesting question, I said without hesitation, a toy inventor! And it’s because I loved creating, putting together new things or giving them a new utility. All of that seemed a lot of fun to me.

Luis Alberto Condori
As an anecdote, I remember that when I was 9 years old, my mother scolded me for destroying the new car toy they gave me. “I will not buy you any more toys since you destroy everything,” she told me. But what she did not realize was why I did it. I was intrigued to know how that little car moved when I dragged it back. At that moment, it did not make sense to me and I was not going to be left with any doubt so I decided to take it apart to see what was going on the inside. I found plastic gears, metal and springs. I took apart many more car toys as I wanted to know if they all worked the same and why some were faster than others. That often happened to me; a question would arise, and I would propose a hypothesis, and I would then carry out one test after another to see if I was right. Years later, I learned that this was called the scientific method and what I had learned about the movement and strength of materials was called mechanics.
I was born in 1993 in Oruro, a small town in Bolivia that is known for its folklore and carnival which was recognized by UNESCO as the Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity.
I studied at the La Salle school where I was taught about the importance of education and values. Virtues that I appreciate to this day.
Broadly speaking, my childhood and adolescence were not very outstanding. I was an ordinary guy and people did not have many expectations for me, or at least that is the impression they had. But I did not think the same.
The good thing about hitting rock bottom is that the only option left is to emerge. And that’s what I did.
When I had to choose my undergrad major, I remembered the dream I had as a child … where do you study to become a toy inventor? This was the question I asked myself. In my search, I found that engineering was the closest thing to it. But why toys? I was not a child anymore. I wanted to be an inventor of toys for 2 simple reasons, I liked the idea of innovating and I wanted my creations to bring smiles to children. I was then convinced and I decided on environmental engineering because I could use the ingenuity of an inventor to build “toys” (aka equipment) that help preserve the environment and thus make many children smile.
I received the support of my parents and in order to fulfill my goal, I moved to the city of La Paz. I enrolled at the Military Engineering School, a private university. I was excited; however, it did not take long for everything to fall apart. My family suffered a severe economic crisis and my mother was diagnosed with kidney failure. This was a hard blow that prevented me from continuing my studies at that university for some time. But my desire to fulfill my goal never ended. I finally started my studies again at the Universidad Mayor de San Andrés (UMSA), a state university.
My mother was hospitalized for almost 2 years during which I had to mature a lot. My life at that point can be summarized as a cycle between school, the hospital and the small room where I lived. After several failed compatibility tests, my father decided to be the donor, and miraculously the surgery was a success. The whole experience taught me the importance of cherishing love and life.
Things started to go back to normal. However, I was not the creative and restless child anymore. I had become a pessimistic, introverted and insecure person.
The good thing about hitting rock bottom is that the only option left is to emerge. And that’s what I did. I structured my studies which helped me perform well in the subjects I liked. I also took several extracurricular courses and volunteered. I had returned to my dreams.
An important milestone for me was participating in Clubes de Ciencia Bolivia. This program sparked my passion in science and technology. The education model they use is different from the conventional one; grades are not the most important thing for the instructors. Instead, they value the potential, the ideas and the intrinsic value of each student. There, I learned that it does not matter how much knowledge you have, but how much you can actually contribute with it.
I learned so many things that I felt the need to apply them. Ever since taking part in the program, I have participated in several competitions across different science branches including climate change, entrepreneurship, technology, sustainable development, education, and more! I am currently a senior in Environmental Engineering, a member of the NGO ECOTEC, and I work in Industry Solutions, a company that helps micro and small business develop by providing industrial machinery and engineering services. Somehow, I feel that I am fulfilling my dream and I am part of a team that builds big toys to make children smile.
[su_boxexpand more_text=”Read more about Luis’ Water Purification Project” link_style=”button”]At the end of 2016, La Paz experienced one of the biggest crises in its history with regard to the supply of drinking water. The crisis was so severe that daily you could see families making long lines for hours to get a bucket of water… constant strikes, hospitals using rainwater, and more. An engineer is the one that uses knowledge and ingenuity to solve problems. Under that concept, we formed a team of 5 people: Mauricio, Joaquin, Grecia, Lizzeth and I. We were all from the UMSA Engineering Faculty. We challenged ourselves to obtain an academic solution to the water crisis we were experiencing. We started to investigate the causes of the crisis and identified 5 which would be interesting to analyze elsewhere.
La Paz, being one of the largest cities and perhaps the most well known in Bolivia, received support from public institutions, private companies and neighboring countries. Unfortunately, rural communities were not that lucky. The water crisis that the city of La Paz went through for a period of approximately 4 months, had actually been going on for years in the rural area and intensifies even more during the dry season. That is why we decided to focus our efforts in this sector. In Bolivia, 32% of the population lives in the rural area and the coverage of drinking water according to the Ministry of Environment and Water is 65%. This means that 35% of the Bolivian population living in rural communities does not have access to potable water, which is equivalent to one million three hundred thousand (1,300,000) people, of which the most vulnerable are children.
According to UNICEF 2012, Bolivia ranks second in Latin America in infant mortality, and each year, 30,000 Bolivian children die due to unsafe water consumption; almost all of them are from rural regions and peri-urban areas. Then the question arises, what is the cause of this situation? We did some research and we came to the conclusion that the problem was not the water deficit itself. Bolivia has enough water resources. The problem is that these water bodies are not suitable for human consumption. And since there are many dispersed rural communities with an average population of 500 inhabitants, it is difficult to implement conventional water purification systems due to a series of limitations. Among them: the shortage of qualified technical personnel to operate systems of this type, low or no availability of required chemical inputs, scarce economic resources and in many cases these communities also lack electricity.
Then we set out to put together a system to overcome these difficulties and we designed and built a prototype that has a source of photovoltaic energy, has easy operation, maintenance, and is affordable. We achieved this by merging and adapting membrane technologies and solar energy. Once our prototype passed the tests and the resulting water met the requirements of the national water quality standards, we traveled to the rural area, and we looked for communities with high infant mortality rates due to unsafe water consumption.
We arrived to Millocato, a town of almost 500 inhabitants that at the time of crisis had no choice but to take water from a river diverted from the Choqueyapu River – one of the most polluted ones in the city of La Paz. It was heartbreaking to see how thirsty children crouched to collect water from a stream from this river. This was water that was originally intended for irrigation. It had yellow-brown coloration and had a slight unpleasant smell. Laboratory tests showed a high degree of turbidity and microbiological contamination.
We installed the prototype at the Millocato school. The teachers welcomed us with joy and the children were paying close attention to what we were doing. According to what they told us, it was not very common to receive visits from strangers in that town. We treated the water from the river I previously mentioned. The difference before and after the treatment was evident. The resulting water didn’t have color, and it didn’t have any smell or particles in suspension. We drank it first, given the previous laboratory tests. We then invited the kids to try it. At the beginning, only 2 brave ones were encouraged to do it. How was it, I asked one of them. “Delicious! You can give me more,” he answered me.
After the litmus test, everyone wanted to taste it. “Calm down, do not fight,” said one of my teammates. Then they lined up so that everyone could quench their thirst. That moment was indescribable, one of the happiest memories I have. The joy of those children was worth all the effort put into this research. Almost a month after that visit, we decided to participate in a scientific fair organized by the Faculty of Engineering.
We obtained second place and a money prize which helped us cover part of the expenses. The project has improved a lot ever since. We have built a second prototype, this time semi-automatic, with a control board and defined stages of production and filter cleaning. We participated in other competitions. We won a small grant from the World Group of Entrepreneurs of New Jersey. We were invited to present our work to the World Student Environmental Network 2017, and recently I had the opportunity to travel to Paraguay to the XXV Conference of Young Researchers of the Association of Universities of Grupo Montevideo, where our research qualified as one of the three best water research projects in South America.
It all started as a school project and now we have become an NGO. We call ourselves Energy and Productive Ecotechnologies (ECOTEC), and our main goal is to provide solutions to rural area’s needs with the help of clean and sustainable technology. The next step is to build a pilot plant to evaluate potential problems that may arise, make the respective improvements, and if we have enough support, to implement it in the communities that need it the most.
This project opened us many doors and little by little we are expanding internationally. Currently, Mauricio is pursuing a master’s degree at the Federal University of Sao Carlos in Brazil. Lizzeth won a scholarship to complete her studies at the University of Buenos Aires, Argentina and I had the opportunity to participate in an research event in Paraguay. I mention this because it is important to emphasize in the importance of teamwork. Each of us fulfilled a role and we were all connected through a common goal: to help others. For us that’s what science and engineering are all about: applying all that knowledge to be able to contribute into something. [/su_boxexpand]
Cover Image is by Remaztered Studio from Pixabay | CC0 Creative Commons
Metrics
Sessions
Total number of Sessions. A session is the period time a user is actively engaged with the page.
Visitors
Users that have had at least one session within the selected date range. Includes both new and returning users.
Page views
Pageviews is the total number of time the article was viewed. Repeated views are counted.
The CS Media Lab is a Boston-anchored civic science news collective with local, national and global coverage on TV, digital print, and radio through CivicSciTV, CivicSciTimes, and CivicSciRadio. Programs include Questions of the Day, Changemakers, QuickTake, Consider This Next, Stories in Science, Sai Resident Collective and more.

-
Audio Studio1 month ago
“Reading it opened up a whole new world.” Kim Steele on building her company ‘Documentaries Don’t Work’
-
 Civic Science Observer1 week ago
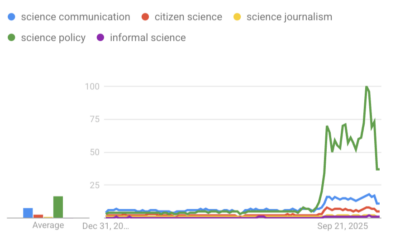
Civic Science Observer1 week ago‘Science policy’ Google searches spiked in 2025. What does that mean?
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Our developing civic science photojournalism experiment: Photos from 2025
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Together again: Day 1 of the 2025 ASTC conference in black and white
Contact
Menu
Designed with WordPress