Stories in Science Special Series
Undeterred: My Journey Continues
Lauren Neal: “Representation in science is of the utmost importance to me at this point in my life. I hope to contribute to changing the idea of what a scientist is supposed to look like or where they are supposed to come from.”

Lauren Neal
[su_boxbox title=”About”]Lauren Neal is currently a rising senior at Agnes Scott College pursuing a BS in Neuroscience with a minor in Chemistry and will be graduating in May 2020. Although she is still early in her scientific career, she strongly believes that the experiences she’s had so far have been imperative in guiding her to where she is today. The story below was edited by Emily Sherman.[/su_boxbox]
[dropcap]I[/dropcap] grew up in the southwest suburbs of Chicago, Illinois, with an architect father, a mother who works in communications, and a younger sister that is currently an aspiring artist. I have been fascinated with figuring out how the world for as long as I can remember, whether it be in terms of life sciences, archaeology, or medicine. As a child I remember asking my mom and dad for space-themed puzzles, children’s fossil digging kits, a “microscope” camera that could attach to my television, and, my personal favorite, a forensics kit that allowed you to dust objects for fingerprints so I could solve imaginary crimes in my house all day. I knew from a young age that I wanted to be in a field that allowed me to use my hands, and ultimately discover something.
In high school I immersed myself in science classes. Once, I even begged the administration to allow me to take three science classes in one year. I was excelling and knew that I had a lot of potential to be great in the future. During my junior year of high school, I took an Anatomy and Physiology course (to prepare for medical school, of course). I discovered the magic that is the human nervous system, and neuroscience in particular. I immediately knew it was the field for me, since I always had an interest in psychology and behavior, but also wanted the hands-on experiences I was getting in my biology and chemistry classes. I could combine these interests in the field of neuroscience. I began to read journal articles so I could learn as much as I could before applying to college the following year. Although I understood very little of the content, I knew it was something I wanted to understand in the future.
I was determined to attend a small liberal arts college with an intended major in neuroscience. During one meeting, I excitedly brought my idea to my high school college counselor, who had always been supportive of me. But then she said the following:
You should do something easier. Neuroscience is not for you.
She went on to tell me that only valedictorians go on to pursue neuroscience, and that I would probably drop out my first semester if I even tried. I will never forget those words. I was floored. My grades were top notch, and I never gave anyone any reason to think that I was incapable of pursuing my dreams. I found myself questioning why it was that she felt so strongly about this.
As a young black woman, I now understand what lead her to make those conclusions about me and my future. There are very few people who look like me in STEM. I am sure she did not know of any scientists of color. It was probably difficult for her to visualize me in that role, which is a sad but unfortunately true reality.
I did not let her deter me, and I stuck to my original plan. College has been a completely life-changing experience for me. I came into college intending to pursue medicine. However, during my first summer, I was awarded the opportunity to conduct research in a summer program sponsored by my college. This project focused on annotating Drosophila genus genes in bioinformatics software. It was exciting not knowing what I would find. For the first time, I was not in a lab associated with a course where the answers are already determined.
I hope to contribute to changing the idea of what a scientist is supposed to look like or where they are supposed to come from.
I currently am participating in the Howard Hughes Medical Institute Exceptional Research Opportunities Program. Through this program I have been doing neuroscience research in the Hobert Lab at Columbia University for the past two summers. This experience combined with presenting at the Annual Society for Neuroscience Conference made the decide to pursue a strictly research-based career, no longer pursuing medicine.
I will be applying to neuroscience PhD programs this upcoming semester. I hope to do research on the cellular mechanisms behind a number of conditions that affect the nervous system. I intend on having my own lab in the future, where I will be able to help the next generation of scientists develop and hone their skills. The mentors I have had thus far have helped me immensely and have allowed me to grow my own skills, so paying that forward in the future is a goal of mine. Representation in science is of the utmost importance to me at this point in my life. I hope to contribute to changing the idea of what a scientist is supposed to look like or where they are supposed to come from.
Metrics
Sessions
Total number of Sessions. A session is the period time a user is actively engaged with the page.
Visitors
Users that have had at least one session within the selected date range. Includes both new and returning users.
Page views
Pageviews is the total number of time the article was viewed. Repeated views are counted.
The CS Media Lab is a Boston-anchored civic science news collective with local, national and global coverage on TV, digital print, and radio through CivicSciTV, CivicSciTimes, and CivicSciRadio. Programs include Questions of the Day, Changemakers, QuickTake, Consider This Next, Stories in Science, Sai Resident Collective and more.

-
Audio Studio1 month ago
“Reading it opened up a whole new world.” Kim Steele on building her company ‘Documentaries Don’t Work’
-
 Civic Science Observer1 week ago
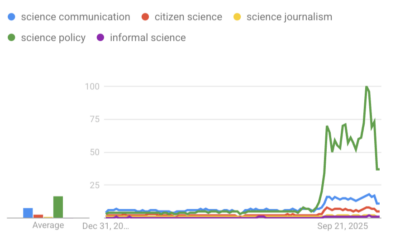
Civic Science Observer1 week ago‘Science policy’ Google searches spiked in 2025. What does that mean?
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Our developing civic science photojournalism experiment: Photos from 2025
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Together again: Day 1 of the 2025 ASTC conference in black and white
Contact
Menu
Designed with WordPress