Civic Science Observer
Science Communication in 2017: A Meta Perspective II
– by Lia Paola Zambetti, PhD | Senior Project Officer | Research Development and Collaboration | The University of Sydney –
[dropcap]I[/dropcap]n the previous installment of “Science communication in 2017: a meta perspective” (click here to read), I discussed some of the main issues that science communication is facing today. In the second and final installment below, I describe why we can look at the future of science communication with optimism. I also discuss a few examples of modern science communication, such as the 3MT competition, and share some thoughts on the so-called “deficit model”.
Despite their seriousness, it is encouraging that the issues discussed in the previous installment of this article1 are now being brought in the open for public debate and discussion – understanding the problem is always the first step to solve it. For a start, academic publishing is undergoing an undercover revolution. New models of peer review and new publication formats, such as open access and pre-publication servers or repositories, are eroding the monopoly of a 200-year old model that, many argue, is in dire need of an update. Open Access, whereby researchers pay for their articles to be published – after which anybody can access them free of charge – is arguably the most effective challenge to the status quo. PLOS, mentioned above, has proved in over 10 years of activity that its business model is sustainable and the majority of traditional publishers have now added open access journals to their offerings. Acknowledging peer review as an activity that should be rewarded in, for example, career advancement or performance review is instead the main goal of Publons2, a website where all reviewers can list their peer-review activity.
Going beyond academic publishing per se, the reproducibility crisis has a far-reaching impact and hugely important consequences, but the volume of the discussion on this topic is rising every day – and so is the attention to it. And the same by and large applies also to risk communication. Hopefully, constant focus will bring forward more debate and some solution in the near future.
Remaining in a specialized setting within academia, there is a growing awareness of the importance of science communication in the new generation of academics in many universities. As an example, the 3MT competition3, where PhD students describe their research in only 3 minutes using lay language, is helping to normalize science communication as an engaging activity for scientists. Many researchers have also taken to Twitter with enthusiasm and zeal, using it both for professional purposes and for communicating with a non-expert audience. It may have to wait for a full generational change perhaps, but it seems that the uptake of science communication by the younger academic generation, especially in places like the UK which have started emphasizing impact some time ago, bodes well for the future.
There are also very promising trends in science communication tout court, i.e., not considering academic publishing or academia only. For a start, Internet opened up access to science communication outlets in a way that would have been unthinkable even 20 years ago. Decreasing the barriers to access has some disadvantages (we mentioned earlier the harsh polarization on some topics) but now literally everyone can write/speak on any topic of interest – and connect with other people interested in the same topic. It can also be argued that the Internet created a space for “funny” science communication (IFLS4 would be a good example for this) that really contributed to bring science closer to a previously disengaged public. And finally, since science is based on aggressive scrutiny and testing, having more pairs of eyes commenting on the latest research from many angles is not necessarily a bad thing either!
A subtler but essential side consequence of this is that a greater number and diversity of science communication voices may contribute to further erosion of the “deficit model5”. This pompous expression is the assumed framework whereby the public is not backing science as it is simply ignorant of the scientific facts/discoveries. According to the model, once more knowledge is supplied by the competent people (i.e., the scientists), support towards science will increase accordingly. However, it has been shown time and time again – that’s not the way it works. More and more science facts will not sway people that hold fast to their convictions, even when these fly in the face of evidence (the anti-vaxxers movement or the climate change deniers come to mind here). Furthermore, such a “lecturing” approach is likely to make the audience, i.e. the public, feel slighted and not on an equal footing as the scientists, leading to resentment – not a good start for any conversation! Not all the belittling of science/science communication is harmful if it pushes towards new forms of engagement between the technical experts (the scientists) and an audience that is equally intelligent and interested but lacks the specialised background.
On this note, we have asked Adam Ruben6, writer, author of the monthly science humor column “Experimental Error” in the journal Science Careers, comedian and molecular biologist, his take on science communication nowadays: “One of the great things about science communication today is that more scientists are practicing speaking like human beings. Don’t get me wrong–the vast majority of science journal articles are incomprehensible to anyone outside the field. But many scientists are starting to realize the value of engaging the public and are volunteering for science cafes, science storytelling, and even something as simple as talking to their child’s class.”
The overall verdict? The situation is in flux. Not so long ago, your choices were limited: to find out about the most recent scientific research, you would have probably read an article on Nature or a small number of similar journals. Nowadays, you have many more options: you might check Twitter or watch a 3-minute presentation on Youtube, look up an open-access journal…all while still reading Nature online. While there are many crisis points in the landscape, there is a lot of experimentation ongoing, a lot of pent-up innovation and, overall, a much larger amount of science simply “out there for grabs” in various formats – so watch this space!
Photo from Pixabay | CC0 Creative Commons
The views expressed in the article are the author’s own.
Links and references:
- https://saicollective.org/2017/09/08/science-communication-2017-meta-perspective/
- https://publons.com/home/
- https://threeminutethesis.uq.edu.au/
- http://www.iflscience.com/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Information_deficit_model
- adamruben.net
The CS Media Lab is a Boston-anchored civic science news collective with local, national and global coverage on TV, digital print, and radio through CivicSciTV, CivicSciTimes, and CivicSciRadio. Programs include Questions of the Day, Changemakers, QuickTake, Consider This Next, Stories in Science, Sai Resident Collective and more.

-
 Audio Studio1 month ago
Audio Studio1 month ago“Reading it opened up a whole new world.” Kim Steele on building her company ‘Documentaries Don’t Work’
-
Civic Science Observer1 week ago
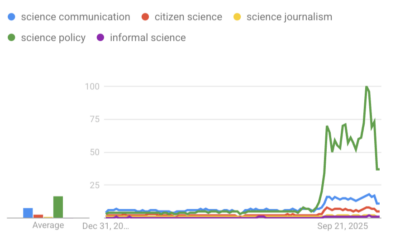
‘Science policy’ Google searches spiked in 2025. What does that mean?
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Our developing civic science photojournalism experiment: Photos from 2025
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Together again: Day 1 of the 2025 ASTC conference in black and white
Contact
Menu
Designed with WordPress