Civic Science Observer
Training: African database for education schemes
by Fanuel Muindi & Moytrayee Guha
– Originally Published in Nature –
[dropcap]T[/dropcap]he severe shortage of trained scientists in Africa (see go.nature.com/gio8pu) has given rise to a variety of programs and initiatives to recruit more students into science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM), and to encourage them to complete their education. A central database that collects and analyses data from all such enterprises is urgently needed to help coordinate their efforts, increase their effectiveness, make them more visible to the public and inform sponsors’ funding decisions.
African science is also beset with systemic problems such as a lack of funding and laboratory equipment, and a pervasive lack of appreciation of the importance of science to a country’s development (see, for example, et al. Nature 474, 556–559; 2011).
Remedial initiatives across the continent include the creation of science and technology institutes, online science networks, science camps, mentoring programmes, scholarships and research fellowships. The proposed database could be modelled on the US STEMconnector, which provides a comprehensive directory and analysis for more than 6,200 STEM programmes across the United States. It is in the interest of African governments, universities and companies to step up and fund this database.
Fanuel Muindi is a former neuroscientist turned civic science ethnographer. He is a professor of the practice in the Department of Communication Studies within the College of Arts, Media, and Design at Northeastern University, where he leads the Civic Science Media Lab. Dr. Muindi received his Bachelor’s degree in Biology and PhD in Organismal Biology from Morehouse College and Stanford University, respectively. He completed his postdoctoral training at MIT.

-
 Audio Studio1 month ago
Audio Studio1 month ago“Reading it opened up a whole new world.” Kim Steele on building her company ‘Documentaries Don’t Work’
-
Civic Science Observer1 week ago
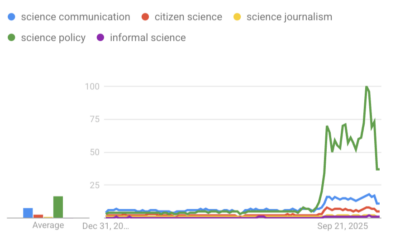
‘Science policy’ Google searches spiked in 2025. What does that mean?
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Our developing civic science photojournalism experiment: Photos from 2025
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Together again: Day 1 of the 2025 ASTC conference in black and white
Contact
Menu
Designed with WordPress