Civic Science Observer
Resuming community science projects after a disaster
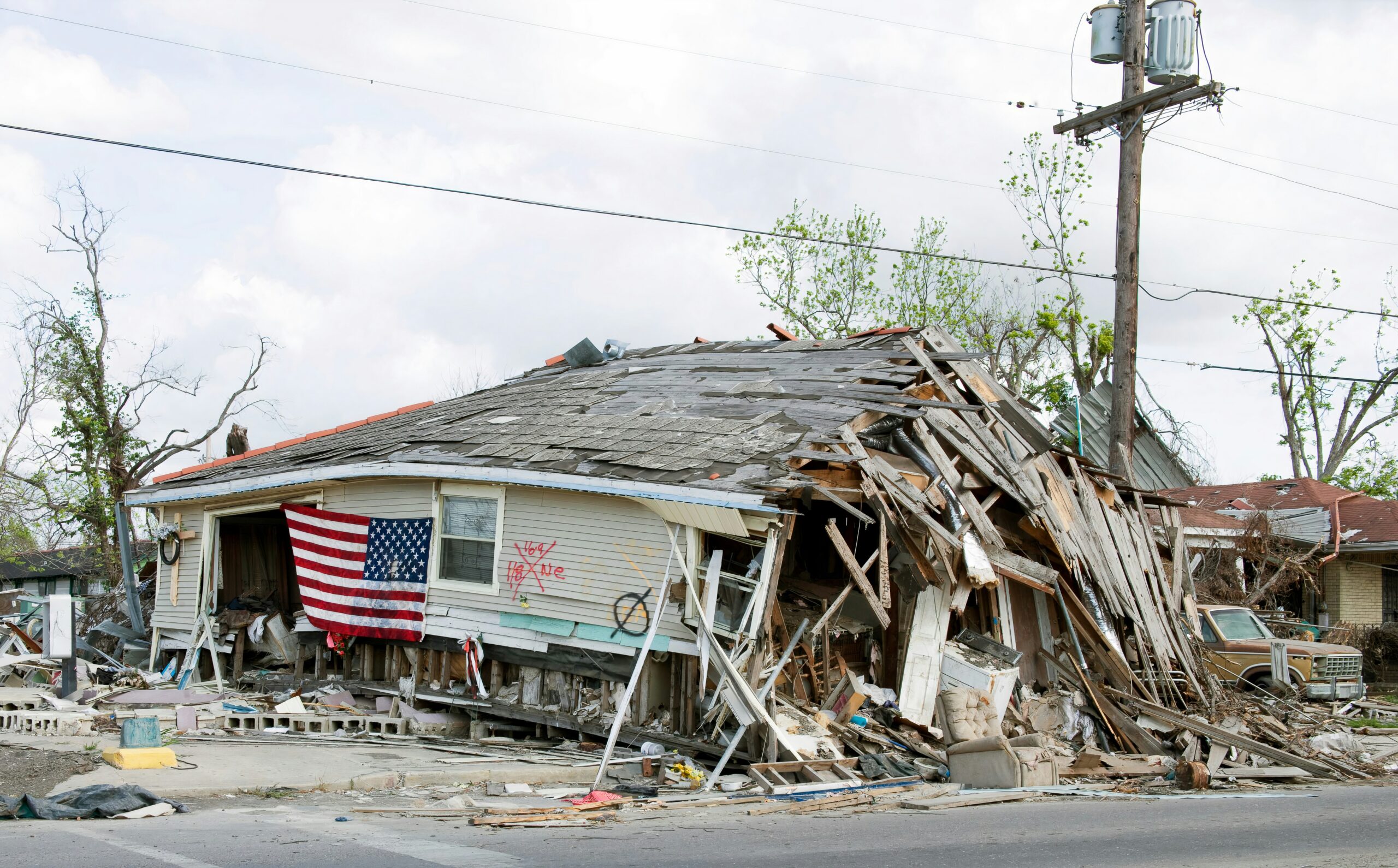

The Great Smoky Mountains Institute at Tremont considers itself fortunate that it was only minimally impacted by Hurricane Helene, which pummeled through six states in late September, killing over 200 people.
Tremont, which is headquartered in Townsend, Tennessee, experienced some impacts, but not like those experienced across the state border in western North Carolina.
“We saw some program cancelations, and we have many friends and family members who were heavily impacted, but our campus and staff were all safe and without damage. We didn’t get anywhere near the rainfall or wind that our neighbors to the east received,” said Erin Rosolina, Tremont’s marketing director. Other than having to cancel or reschedule some butterfly education dates due to poor weather conditions, Tremont experienced no effects.
Sometimes though, research institutions aren’t so lucky. When a community science project encounters a major disruption as a result of an extreme weather event or some other disturbance, one of the first priorities for research organizations is to ensure that public scientists and volunteers are safe, groups told Civic Science Times.
“Having a participatory science component to a research project, or community members being the guiding force of a project, absolutely adds complexity to the project’s recovery,” said Rachael Leta-Graham, participatory science coordinator for the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Region 2.
“First and foremost, those participatory scientists are usually the ones affected by the disruptive event, such as a hurricane. It’s hard for your focus to be on the science when you no longer have electricity, running water, or communication with friends and loved ones outside of your neighborhood,” Leta-Graham said.
She continued: “Just as you’re taught to put on your own oxygen mask before helping others on a plane, those folks need to take care of themselves and their communities before any work can resume. Sometimes the research work may coincide with recovery needs, and in those cases I’m sure the research gets on track much faster, but it also might see a huge shift in community focus now that there’s been a disruption.”
Carole Nash, a faculty member at James Madison University in Harrisonburg, Virginia, agreed. Nash’s expertise includes Middle Atlantic archaeology, long-term climate change impacts on human community, and science and the public.
“It is my experience in Virginia that often the members of the public who are engaged in citizen science projects are also the first to volunteer in their communities when disasters occur. Because they prioritize disaster relief and recovery, their focus is generally not on the scientific project until after the community is stabilized,” Nash said. “For those of us engaged in the field sciences and who have on-the-ground knowledge of these places — and have developed good working relationships with community members — we would not want it any other way.”
When scientists and researchers are ready to get back to work, they may face a long road ahead. The first step of that journey is to check on the site.
“As soon as the storm clears and study areas are accessible, our citizen scientists will try to get to the sites we’ve identified as soon as possible to assess the damage, if the sites are still there,” Nash said.
The ability to restart field projects after a disaster will depend on access to the site. “What happened in western North Carolina is an extreme example, but road access is often compromised in disaster situations and can delay field projects, even for local community members who are part of a citizen science project,” Nash said.
Once it’s been determined that access is possible, the next steps may include determining what is salvageable—and what isn’t.
“As you might expect, the greatest overall impact to field projects is the loss of the study area. Archaeological sites can be buried under mass movement events or thick deposits of alluvium, or they can be completely scoured away,” Nash said. “Usually, a citizen science project is general enough so that new study areas can be established with the help of local project members, but there are times when a project will come to an abrupt end because of a natural disaster.”
Sometimes, if a major disruption appears to have impacted the research, the scientists or researchers must make the decision to pivot.
“We also deal with the fact that natural disasters can expose previously unknown sites, so I’ve seen citizen science efforts shift to survey so that these are documented,” Nash said.
Indeed, that’s what may happen in western North Carolina and other Helene-impacted regions along the road to recovery.
“I think we’re all curious to learn more about how this storm affects the ecological communities in our region,” Tremont’s Rosolina said.
Joanna Marsh is a freelance writer and journalist based in Washington, D.C. For The Civic Science Observer, she reports on new developments across the citizen science landscape, covering both new research and on-the-ground practice. Her work highlights how local communities are engaging with scientists to contribute to ongoing scientific research and lessons being learned by the involved stakeholders.

-
 Audio Studio1 month ago
Audio Studio1 month ago“Reading it opened up a whole new world.” Kim Steele on building her company ‘Documentaries Don’t Work’
-
Civic Science Observer1 week ago
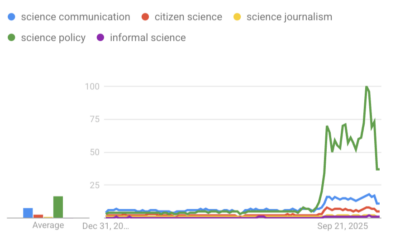
‘Science policy’ Google searches spiked in 2025. What does that mean?
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Our developing civic science photojournalism experiment: Photos from 2025
-
Civic Science Observer1 month ago
Together again: Day 1 of the 2025 ASTC conference in black and white
Contact
Menu
Designed with WordPress